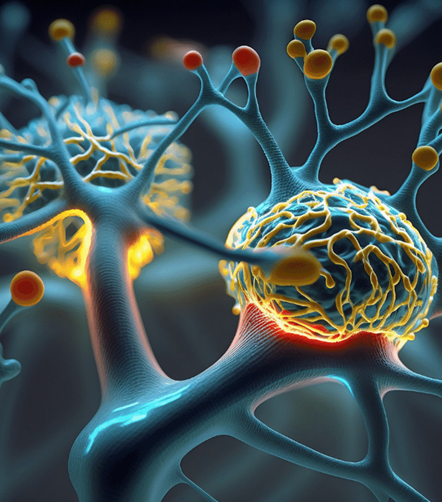
The human brain, a marvel of biological engineering, is not just the control center of our body; it's also a dynamic, adaptable, and incredibly resilient organ. Neuroplasticity, or brain plasticity, is a term that captures the brain's ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life. This ability is not just fascinating from a scientific standpoint but also profoundly impactful on our daily lives.
Neuroplasticity: The Brain's Adaptive Power
At its core, neuroplasticity is about adaptation. Whether in response to learning, experience, or injury, the brain's neural networks can rewire and strengthen, demonstrating a flexibility that was once thought impossible. This adaptability is crucial for recovery from brain injuries and is also the mechanism behind learning new skills and adapting to new situations.
The brain's plasticity is influenced by several factors, including genetics, environment, and lifestyle. Activities that challenge the brain, such as learning a new language, playing a musical instrument, or engaging in complex problem-solving, can enhance this plasticity, leading to improved cognitive function and a healthier brain.
The Role of Neuroplasticity in Learning and Memory
Learning and memory are perhaps the most striking examples of neuroplasticity at work. When you learn something new, your brain changes physically. Neurons (nerve cells in the brain) forge new connections, and existing pathways become stronger or weaker depending on their usage. This dynamic process not only helps in storing new information but also in making it accessible for future use.
For instance, when you practice playing the piano regularly, the areas of the brain involved in music and coordination grow larger and more active. This is the brain adapting to the demands placed on it, a process known as synaptic plasticity.
Recovering from Brain Injury
Neuroplasticity plays a critical role in the brain's ability to recover from injury. When parts of the brain are damaged, the areas of the brain that remain intact can take over some of the lost functions through a process known as brain reorganization. This is why individuals who suffer from strokes or traumatic brain injuries can regain skills and improve over time with physical therapy and practice.
The brain's ability to rewire itself does have limits, but its capacity for change is a beacon of hope for many patients and their families. It underscores the importance of rehabilitation and consistent practice in recovery from brain injury.
Adapting to New Experiences
Every new experience can alter the brain's structure and function. This includes not only learning skills or recovering from injuries but also adapting to new environments. For example, if you move to a high-altitude area, your brain can adapt to lower oxygen levels; or if you start a new job that requires a different sleep schedule, your brain gradually adjusts to the new routine.
This adaptability is crucial for survival and efficiency in diverse environments and situations. It allows humans to thrive in a variety of settings, from bustling cities to secluded natural environments.

Enhancing Neuroplasticity: Tips for a Healthier Brain
Given the importance of neuroplasticity, there are several ways to enhance this natural capability of the brain:
- Continuous Learning: Engage in new activities that challenge your brain. Learn a new skill, read regularly, or play brain-stimulating games.
- Physical Exercise: Regular physical activity increases blood flow to the brain, which can help improve cognitive functions and encourage the growth of new neural connections.
- Healthy Diet: Omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and nutrients like flavonoids and polyphenols promote brain health. Foods rich in these nutrients include fish, berries, nuts, and green leafy vegetables.
- Adequate Sleep: Sleep is crucial for brain health. It helps consolidate memories and clear out toxins that accumulate in the brain during the day.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practices like meditation, yoga, and mindfulness can reduce stress and enhance concentration and memory by fostering new connections in the brain.
The Future of Neuroplasticity
As research in the field of neuroplasticity advances, the potential applications in medicine, psychology, and even education continue to expand. Understanding how the brain changes in response to interventions can lead to better therapies for mental health disorders, more effective learning programs, and innovative ways to maintain cognitive function as we age.
The brain's ability to adapt and reorganize itself is a testament to the resilience and potential of the human mind. By fostering a better understanding of neuroplasticity, we can not only improve individual health and recovery but also enhance the collective human experience.

May we say in conclusion...
Neuroplasticity is not just a scientific concept but a phenomenon that touches every aspect of our lives. It shapes how we learn, adapt, and overcome challenges, making it a fundamental factor in our lifelong development and well-being. Embrace the power of your brain and consider how you can influence your own neuroplasticity for a sharper, more resilient mind.

Neuroplasticity FAQs
What is neuroplasticity and why is it important?
Neuroplasticity, or brain plasticity, is the brain's ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life. This adaptability is crucial as it enables the brain to evolve continuously, helping us learn new skills, recover from injuries, and adapt to various life experiences.
How does neuroplasticity affect learning and memory?
Neuroplasticity plays a fundamental role in learning and memory by strengthening the neural connections that are frequently used and weakening those that are rarely engaged. This dynamic allows for the efficient storage and retrieval of information, enhancing learning processes and memory retention over time.
Can neuroplasticity help in recovering from brain injuries?
Yes, neuroplasticity is key in the recovery process from brain injuries. By forming new connections and utilizing undamaged areas of the brain, neuroplasticity can compensate for lost functions and improve cognitive and physical capabilities post-injury.
What factors influence neuroplasticity?
Several factors can influence the rate and extent of neuroplasticity, including age, environment, behavior, and experiences. Engaging in new learning activities, physical exercise, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are known to positively impact neuroplasticity.
Are there ways to enhance neuroplasticity?
Enhancing neuroplasticity can be achieved through various activities that challenge the brain and body. This includes learning new skills, languages, or musical instruments, engaging in regular physical exercise, practicing mindfulness and meditation, and ensuring a diet rich in nutrients that support brain health.